
The position of the focus of a parabolic dish antenna (or parabolic reflector) can be determined in terms of the diameter and depth of the dish.
The equation of a parabola can be written to explicitly show the focal distance \(f\) (distance from the vertex to the focus).
Consider a parabola with focus \(F(0,f)\) and directrix \(y=-f\):

By the definition of a parabola, any point \(M(x,y)\) on the parabola is equidistant from the focus and the directrix:
\[ \sqrt{(x-0)^2 + (y-f)^2} = \sqrt{(x-x)^2 + (y-(-f))^2} \]Squaring both sides and simplifying gives the standard equation in terms of the focal distance \(f\):
\[ x^2 + y^2 + f^2 - 2yf = y^2 + f^2 + 2yf \quad \Rightarrow \quad y = \frac{x^2}{4f} \]For a parabolic dish of diameter \(D\) and depth \(d\), the parabola passes through the points \((D/2, d)\) and \((-D/2, d)\). Using the parabola equation:
\[ d = \frac{(D/2)^2}{4f} \quad \Rightarrow \quad f = \frac{D^2}{16d} \]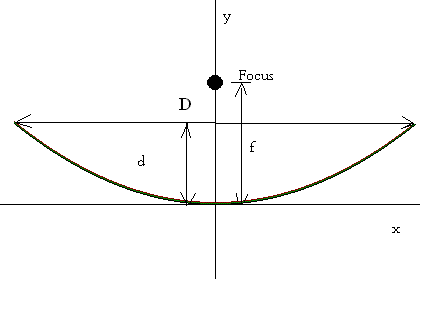
This formula is used to position the feed of the parabolic antenna. In practice, minor adjustments are often needed as dishes are not perfectly parabolic.
A Parabolic Reflector Focus Calculator is available online for convenience.