
First, we review the definition of inverse functions. Then we investigate the graphs of one-to-one functions and their inverses. More tutorials on finding inverse functions are included.
Let a function \(f\) be defined as a set of ordered pairs:
\[ f = \{(-3, 0), (-1, 1), (0, 2), (1, 4), (5, 3)\} \] The inverse function \(g\) of \(f\) is obtained by interchanging the components of each ordered pair: \[ g = \{(0, -3), (1, -1), (2, 0), (4, 1), (3, 5)\} \]

The plots of \(f\) and \(g\) are shown below. Function \(f\) and its inverse \(g\) are reflections of each other on the line \(y = x\).

The inverse function of a one-to-one function \(f\) is denoted by \(f^{-1}\) and defined as:
Note: The \(-1\) in \(f^{-1}\) is not a power.
If \(f\) is not one-to-one, it does not have an inverse function.
Example: Let \[ f = \{(1,0),(4,5),(6,9)\} \] Then the inverse is \[ f^{-1} = \{(0,1),(5,4),(9,6)\} \] The domain of \(f\) is the range of \(f^{-1}\), and the range of \(f\) is the domain of \(f^{-1}\).
In general: \[ f(f^{-1}(x)) = x, \quad x \in \text{domain of } f^{-1} \] \[ f^{-1}(f(x)) = x, \quad x \in \text{domain of } f \]
In some situations, we know the output of a function and need to find the input. For example, solve for \(x\) such that \(0 < x < \pi/2\):
\[ \sin(x) = 0.2 \implies x = \arcsin(0.2) \] Here \(\arcsin\) is the inverse of \(\sin\).
Only one-to-one functions are invertible. For example: \[ f = \{(-3,0), (-1,2), (0,2), (1,4), (5,3)\} \] The inverse would be \[ g = \{(0,-3),(2,-1),(2,0),(4,1),(3,5)\} \] But \(g\) is not a function because input 2 has two outputs (-1 and 0). Therefore, \(f\) is not invertible.


Graphs of functions (blue) and their inverses (red):
For each function graphed below: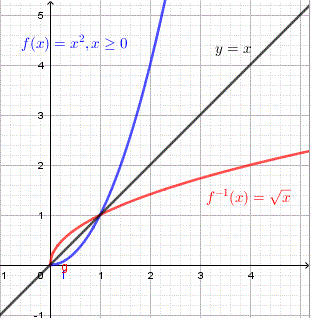 b)
b)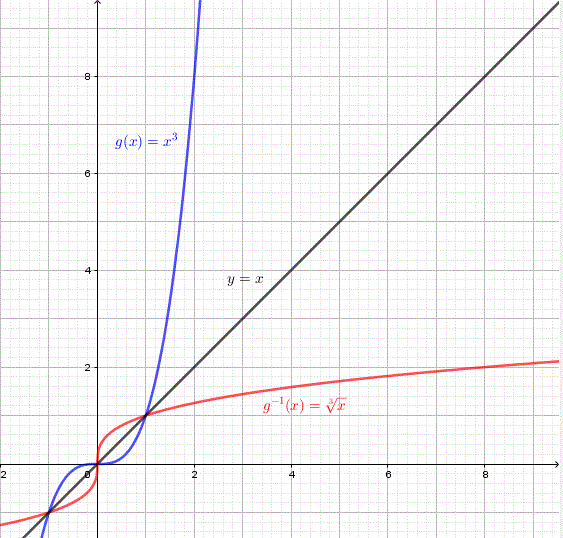 c)
c)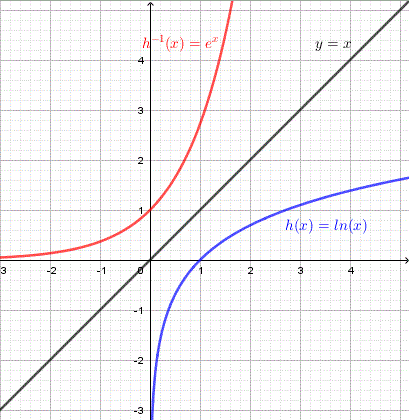
a) \(f(x) = x^2, x \ge 0\) Points on \(f\): \((0,0),(1,1),(2,4)\) Points on \(f^{-1}\): \((0,0),(1,1),(4,2)\)
b) \(g(x) = x^3\) Points on \(g\): \((-1,-1),(0,0),(1,1),(2,8)\) Points on \(g^{-1}\): \((-1,-1),(0,0),(1,1),(8,2)\)
c) \(h(x) = \ln(x)\) Points on \(h\): \((1,0),(4,1.4)\) Points on \(h^{-1}\): \((0,1),(1.4,4)\)
Exercise 1: Find the domain and range of \[ f = \{(-4,2),(-3,1),(0,5),(2,6)\} \] Find its inverse and domain and range.
Exercise 2: Identify functions without inverses: \[ f = \{(-1,2),(-3,1),(0,2),(5,6)\},\quad g = \{(-3,0),(-1,1),(0,5),(2,6)\},\quad h = \{(2,2),(3,1),(6,5),(7,1)\} \]
Exercise 1: Domain of \(f = \{-4,-3,0,2\}\), Range of \(f = \{2,1,5,6\}\) Inverse: \(f^{-1} = \{(2,-4),(1,-3),(5,0),(6,2)\}\) Domain of \(f^{-1} = \{2,1,5,6\}\), Range of \(f^{-1} = \{-4,-3,0,2\}\)
Exercise 2: Functions \(f\) and \(h\) are not one-to-one; they do not have inverses.